Together with average tallies, TRIPOLI-4® allows also for two legacy perturbation schemes, namely
- the correlated sampling method and
- the Taylor series development (differential operator sampling).
The key idea behind the correlated sampling is the following [1]: if we want to estimate the effect of a perturbation on a reaction rate or on any quantity of interest, whenever we increment the contribution to the unperturbed score by a quantity s, we have to increment the perturbed score by an amount equalt to the product of the quantity times a likelihood factor, based on the explicit functional form of the perturbed versusn unperturbed operators.
In criticality simulation mode we also have to propagate the perturbation through fission generations, so as to take into account the modification of the source distribution due to the perturbation. For the correlated sampling method, the parameters that can be perturbed are concentrations, densities and cross-sections.
The tallies that can be perturbed are fluxes, reaction rates and the multiplication factor.
Differential operator sampling [2] has been implemented in TRIPOLI-4® up to the second order in the Taylor expansion, including cross derivatives. Since the derivatives are calculated once for all, differential sampling is particularly suited for sensitivity analysis. Differential sampling is in good agreement with correlated sampling if cross derivatives are included in the Taylor expansion. Differential sampling allows perturbing concentrations and densities in fixed-source calculations.
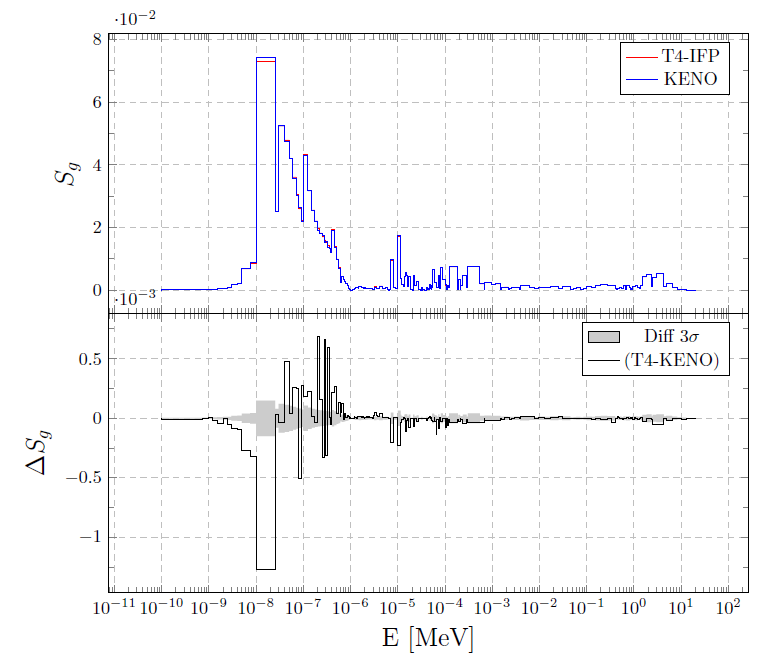
Computing the sensitivity of keff to fission neutron yield (MIX-COMP-THERM-001-001).
In addition to correlated sampling and differential operator sampling, TRIPOLI-4® can furthermore compute reactivity perturbations, and sensitivities of the multiplication factor, of ratios of reaction rates and of kinetics parameters to nuclear data via Iterated Fission Probability (IFP) methods or super-history-based methods. For the sensitivity of the kinetics parameters, the Differential Operator Sampling method is used. Such methods are implemented via the reference calculation of the critical adjoint flux, which is used in order to weight the operators appearing in the bilinear forms required by the Standard Perturbation Theory [3] and by the Generalized Perturbation Theory [4].

Sensitivity profile of the F28/F25 reaction rate ratio (fission cross section) on 235U for the UAM TMI pin-cell benchmark. Comparison between TRIPOLI-4 and SCALE results.